Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career.

Everything You Need To Master Financial Modeling
One common misconception pertains to the difference between the CM and the gross margin (GM). A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site.
Contribution Margin Vs Gross Margin
Fixed costs include periodic fixed expenses for facilities rent, equipment leases, insurance, utilities, general & administrative (G&A) expenses, research & development (R&D), and depreciation of equipment. Direct materials are often typical variable costs, because you normally use more direct materials when you produce more items. In our example, if the students sold 100 shirts, assuming an individual variable cost per shirt of $10, the total variable costs would be $1,000 (100 × $10). If they sold 250 shirts, again assuming an individual variable cost per shirt of $10, then the total variable costs would $2,500 (250 × $10).
- We’ll next calculate the contribution margin and CM ratio in each of the projected periods in the final step.
- The more customers she serves, the more food and beverages she must buy.
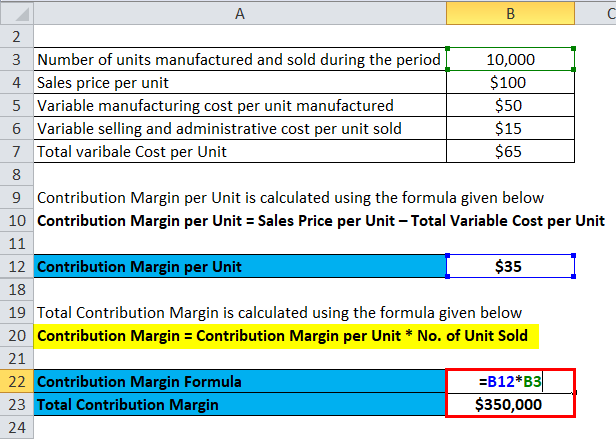
- Using the provided data above, we can calculate the price per unit by dividing the total product revenue by the number of products sold.
- A university van will hold eight passengers, at a cost of $200 per van.
- After variable costs of a product are covered by sales, contribution margin begins to cover fixed costs.
- There is no definitive answer to this question, as it will vary depending on the specific business and its operating costs.
Calculating the Contribution Margin and Ratio
Aside from the uses listed above, the contribution margin’s importance also lies in the fact that it is one of the building blocks of break-even analysis. With that all being said, it is quite obvious why it is worth learning the contribution margin formula. You need to fill in the following inputs to calculate the contribution margin using this calculator. As you can see, the contribution margin per-unit remains the same. Accordingly, the per-unit cost of manufacturing a single packet of bread consisting of 10 pieces each would be as follows.
In this chapter, we begin examining the relationship among sales volume, fixed costs, variable costs, and profit in decision-making. We will discuss how to use the concepts of fixed and variable costs and their relationship to profit to determine the sales needed to break even or to reach a desired profit. You will also learn how to plan for changes in selling price or costs, whether a single product, multiple products, or services are involved.
Disadvantages of Contribution Margin
The higher the number, the better a company is at covering its overhead costs with money on hand. The contribution margin ratio is calculated as (Revenue – Variable Costs) / Revenue. Investors examine contribution margins to determine if a company is using its revenue effectively. A high contribution margin indicates that a company tends to bring in more money than it spends. Say a machine for manufacturing ink pens comes at a cost of $10,000. A low margin typically means that the company, product line, or department isn’t that profitable.
The business can interpret how the sales figures are affecting the overall profits. Similarly, we can then calculate the variable cost per unit by dividing the total variable costs by the number of products sold. Companies often look at the minimum price at which a product could sell to cover basic, fixed expenses of the business.
Let us try to understand the concept with a contribution margin example. Get instant access to video lessons taught by experienced investment bankers. Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts.
Other financial metrics related to the Contribution Margin Ratio include the gross margin ratio, operating margin ratio, and net profit margin ratio. These ratios provide insight into the overall profitability of a business from different perspectives. A company has budgeted sales of $200,000, a profit of $60,000 and fixed expenses of $40,000. Investors and analysts use the contribution the difference between net 30 and due in 30 days margin to evaluate how efficient the company is at making profits. For example, analysts can calculate the margin per unit sold and use forecast estimates for the upcoming year to calculate the forecasted profit of the company. When the contribution margin is calculated on a per unit basis, it is referred to as the contribution margin per unit or unit contribution margin.

